2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz WiFi
What is the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz WiFi? Today, we will be discussing the differences between the two wireless frequencies and when to use them.
When someone refers to a device as being dual-band, the term indicates that the device has the capability of broadcasting both a 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz frequency. The 2.4 GHz radio runs on a lower frequency between 450 Mbps or 600 Mbps. The 5.8 GHz radio can support up to 1300 Mbps. That’s a pretty big difference in wireless speed.
Most devices in your home, including cordless telephones, Bluetooth devices, garage door openers and even baby monitors, run on the 2.4 GHz frequency. The 5.8 GHz frequency, which is a newer standard, is not commonly used in these devices so, dual-band routers are less likely to see interference, from common household devices and access points, on the 5.8 GHz frequency. When multiple devices or access points attempt to use the same radio space, overcrowding occurs. The 5.8 GHz band tends to be less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band because fewer devices use it and because it has 23 channels for devices to use, while the 2.4 GHz band has only 11 channels available. The number of channels that are available to you depends on the regulatory domain for your location.
Here are a few facts about each frequency:
2.4 GHz
- Majority of devices use 2.4 GHz
- Has the greatest distance
- Can be crowded because of so many users (may affect speed)
- May get interference from other devices running on the same band (i.e. microwaves, cordless phones etc.)
5.8 GHz
- Smaller area of coverage, but usually better speed
- Many devices do not have 5.8 GHz available
- Best way to achieve optimum WiFi performance
- Less range may require more access points for large areas
- Can cause connection issues if all devices are not running on 5.8 GHz
- Preferred for gaming and file streaming because of speed
Here are a few more facts regarding dual-band devices:
802.11g = the device will only operate on 2.4 GHz
802.11n = the device will always operate on 2.4 GHz and some may operate on 5.8 GHz
802.11ac = the device will only operate on 5.8 GHz802.11n is currently used in most devices. Newer devices that use 802.11ac typically offer the option to use 802.11n as well.
For MAC users, Apple offers dual-band wireless on the majority of their products. When purchasing a product, be sure to check the specs on their comparison charts. They will list the capability of each device.
It is ultimately up to the user which frequency they decide to use. Weigh the pros and cons of each connection, see what is available to you and what will give you the optimum performance and range.
I have listed instructions below to check if your windows device is compatible with the 5.8 GHz frequency.
1. Search "cmd" in the Windows Start Menu (Example is using Windows 10)

2. Open the command prompt and Type "
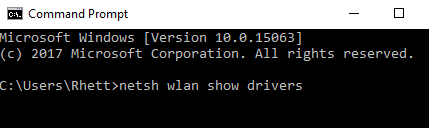
3. Look for the "Radio types supported" section.
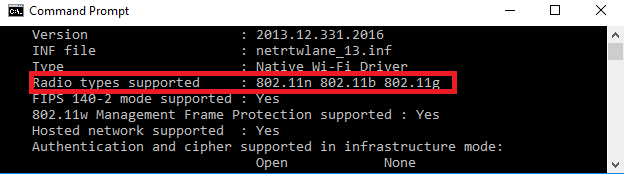
Determining Factor:
If the network adapter supports network mode 802.11ac:
- The computer has 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz network capability and is dual-band compatible.
If the network adapter supports network mode 802.11n:
- The computer may or may not have 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz network capability and be dual-band compatible.
If the network adapter does not support either of these network modes it is not dual-band compatible.
To verify if an Apple laptop or desktop is compatible with 5.8 GHz frequencies follow these steps:
- Hold down the Option key and click on the Apple menu
- Choose “System Information”
- Select “Network” from the left side list of system details, then browse the interface’s list to find “Supported PHY Modes” for the active wireless network card.
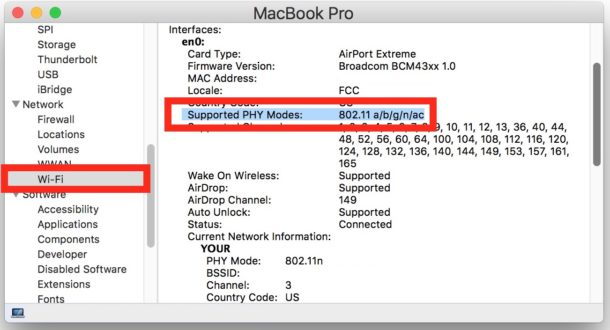
Determining Factor:
If the network adapter supports network mode 802.11ac:
- The computer has 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz network capability is dual-band compatible.
If the network adapter supports network mode 802.11n:
- The computer may or may not have 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz network capability and be dual-band compatible.
If the network adapter does not support either of these network modes it is not dual-band compatible.
In closing, the primary differences between the two frequencies are the range (coverage) and bandwidth (speed) that the bands provide. The 2.4 GHz band provides a wider range of connection but transmits data at slower speeds. The 5.8 GHz band provides a smaller range of coverage but typically transmits data at faster speeds.
Recent Posts
-
What You Need to Know to Donate Safely Online
Cybersecurity has become an increasingly critical issue in the digital age. For instance, in 2016, m …Mar 10th 2022 -
What is a Default Gateway?
A default gateway is where all your internet traffic goes first before leaving your network. That’s …Jan 4th 2022 -
Essential Cybersecurity Tools Every Business Needs
IT infrastructures across organizations are now more complex than ever. Given the increasing number …Nov 29th 2021




